
Scientific Publications
To see the abstract of each article, roll your mouse over the authors' names (in blue. If you have trouble accessing a copy of an article, please email Adrian Treves.
Free downloads throughout this page
Why use pre-prints?
To reach a larger number of peer scientists before an article goes through the publication process, we present our work in pre-print format. For the purpose of collegial discussion and debate, please ask us before re-posting our pre-prints. Also, please inform us if you post a critique of our work so we benefit from the discussion. If we don't know about your response or critique it defeats the purpose of pre-prints. Thanks!
This also has the advantage of reaching the public and policy-makers more quickly. The downside is if we get something wrong (demonstrated by peer-reviewed work or a pre-print shared with us) yet it reached the public and went into effect. We accept that risk because of the pressing public need for scientific information for public policy. We will clearly communicate any corrections if we find an error.
A new pre-print about lethal control interventions intended to protect domestic animals from wolves Adrian Treves, Dror Ben-Ami, Ari M. Cornman, Martin Dul'a, Igor Khorozyan, Miha Krofel, Miroslav Kutal, José Vicente López-Bao, Rona Nadler Valency, Shlomo Preiss-Bloom, Francisco J. Santiago-Ávila, J. Šuba, Agrita Žunna Inadequate evidence that removing wolves prevents domestic animal losses. agriRxiv 2025. 20250243183 https://doi.org/10.31220/agriRxiv.2025.00327.
Louchouarn NX, Renn, E. J., Anderson, G., Parsons, D. R., Putrevu, K., Santiago-Ávila, F. J., & Treves, A. Mexican wolf management needs transparency in methods and data to support policy decisions. J Appl Ecol. 2025;00:1-7 link.
Treves, A., Fisher, A.R. 2026.
A code of ethics for peer reviewers. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial)Early view 2026 https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.70032.
A court decision on endangered species holds lessons for us all. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial) 23(8): https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.70006.
What is a wildlife trustee? And how should one act? A white paper by Treves, A. And Parsa, K. In preparation for peer review. This is a DRAFT of an evolving document intended for collegial discussion. Please contact the authors by Email: atreves [at] wisc.edu and kavya.parsa [at] gmail.com, if you would like to cite this or quote it in a publication.
Published
Treves, A. Robinson, K. 2025. Defining science-informed decision-making. A white paper prepared for Wildlife for All and wildlife advocates seeking to reform wildlife policy anywhere in the world.
Crabtree RL, Conner MC, Treves A.2025. Misleading biases in methods for estimating wolf abundance using spatial models. Academia Biology, 3(4):1-20. https://doi.org/10.20935/AcadBiol7924.
Authors declare no competing interests—really? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial) June 2024.
Letter to the editor rebutting Petracca et al. 2024 on Washington state wolf forecasts. Santiago-Ávila F, vonHoldt BM, Treves A. 2024. Petracca et al. (2024) under-estimates the risk of gray wolf extinction by unscientific value judgments. Biological Conservation 299:110760.
Karann Putrevu's PhD dissertation, entitled Large Carnivores: Case studies on nonlethal effects, population monitoring, and responses to prey depletion.
Brian Schuh's PhD dissertation, entitled "An Experimental Evaluation of Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) Reactions to Sound Playbacks of Domestic Animals and Correlations between Humans’ Attitudes towards Carnivores and their Accuracy of Species Identification.
Alicia Alexandra Pineda Guerrero's PhD dissertation, entitled Human-Carnivore Coexistence: The Functional and Perceived Effectiveness of Solar Lights, and Attitudes Toward Jaguars and Pumas in Colombia .
Naomi Louchouarn's PhD dissertation entitled Don’t judge the roar by its echo: Tests of assumptions, tools and policies for human-carnivore coexistence in North America.
Francisco Santiago-Ávila's PhD dissertation was composed of two published chapters (see below for his lead authorship of two articles in 2018) and a single chapter on animal ethics and philosophy, see Santiago-Avila FJ, Lynn WS. Bridging compassion and justice in conservation ethics. Biol Conserv. 2020;248:108648.
Omar Ohrens' PhD dissertation, entitled Coexistence between people and carnivores in Chile.
Louchouarn, NX, Proulx, G, Serfass, TL, Niemeyer, CC, Treves, A. 2024. Best management practices for trapping are neither best science nor best management. Canadian Wildlife Biology & Management 13(1): 35-49
Robust inference and errors in studies of wildlife control. Scientific Reports 15:33131. https://rdcu.be/eIjAu
Peer-reviewed or published with editorial review
Treves, A., Agan, SW, Langenberg, JA, Lopez-Bao, J.V., Louchouarn, NX. Parsons, DR, Rabenhorst, MF, Santiago-Ávila, FJ, 2024. Response to Roberts, Stenglein, Wydeven, and others. Journal of Mammalogy 2024 in 105(6):1473–1479.
Treves A, Fergus, AR, Hermanstorfer, SJ, Louchouarn, NX, Ohrens, O, Pineda Guerrero, AA. 2024.
Gold-standard experiments to deter predators from attacking farm animals. Animal Frontiers 14(1)"40-52.
After years of research, our conclusions about non-lethal deterrents and how to design randomized, controlled trials with crossover design.
(1) The long-held belief that randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) are impossible in wild ecosystems with working livestock is laid to rest.
(2) Crossover designs reduce most confounding variables between subjects and strengthen inference beyond the gold-standard of RCTs, yet we describe limitations precisely.
(3) Non-lethal methods can be effective in preventing carnivore approaches and attacks on working livestock in fenced pastures or open rangelands. The relationship between approaches and attacks remains uncertain.
(4) Lethal methods of predator control have been subjected to less robust study designs that suggest mixed results including increases in livestock losses.
(5) Non-lethal methods promise the elusive triple-win for wildlife, domestic animals, and livelihoods.
Replace the ivory tower with the fire tower. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial) p.355, doi:10.1002/fee.2676
Rogers A, Treves A, Karamagi R, Nyakoojo M, Naughton-Treves, L. 2023
Trenches reduce crop foraging by elephants: Lessons from Kibale National Park, Uganda for elephant conservation in densely settled rural landscapes. PLoS One 18(7): e0278501.
Western Colorado carnivore coexistence: Gold-standard non-lethal deterrent experiments and human-carnivore coexistence in Montrose, Colorado. Master's thesis, June 2023, Carnivore Coexistence Lab, Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Treves, A., L. M. Elbroch, J. T. Bruskotter, 2024.
Evaluating fact claims accompanying policies to liberalize the killing of wolves, peer-reviewed Chap. 6, pp 159-180. Alpha Wildlife Publications, Canada.
Elbroch L & Treves A. (equal co-authors) 2023.
Why might removing carnivores maintain or increase risks for domestic animals? Biological Conservation 283:110106.
Treves, A., Santiago-Ávila, F.J. 2023
Estimating wolf abundance with unverified methods. Academia Biology 1 doi 10.20935/AcadBiol6099 Compressed source documents
from the state (WDNR 2022 population reports, greensheet and Stauffer et al. 2021).
'Best available science' and the reproducibility crisis. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial) 20(9):495, https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.2568
The infographic below refers to information contained in the above articles.
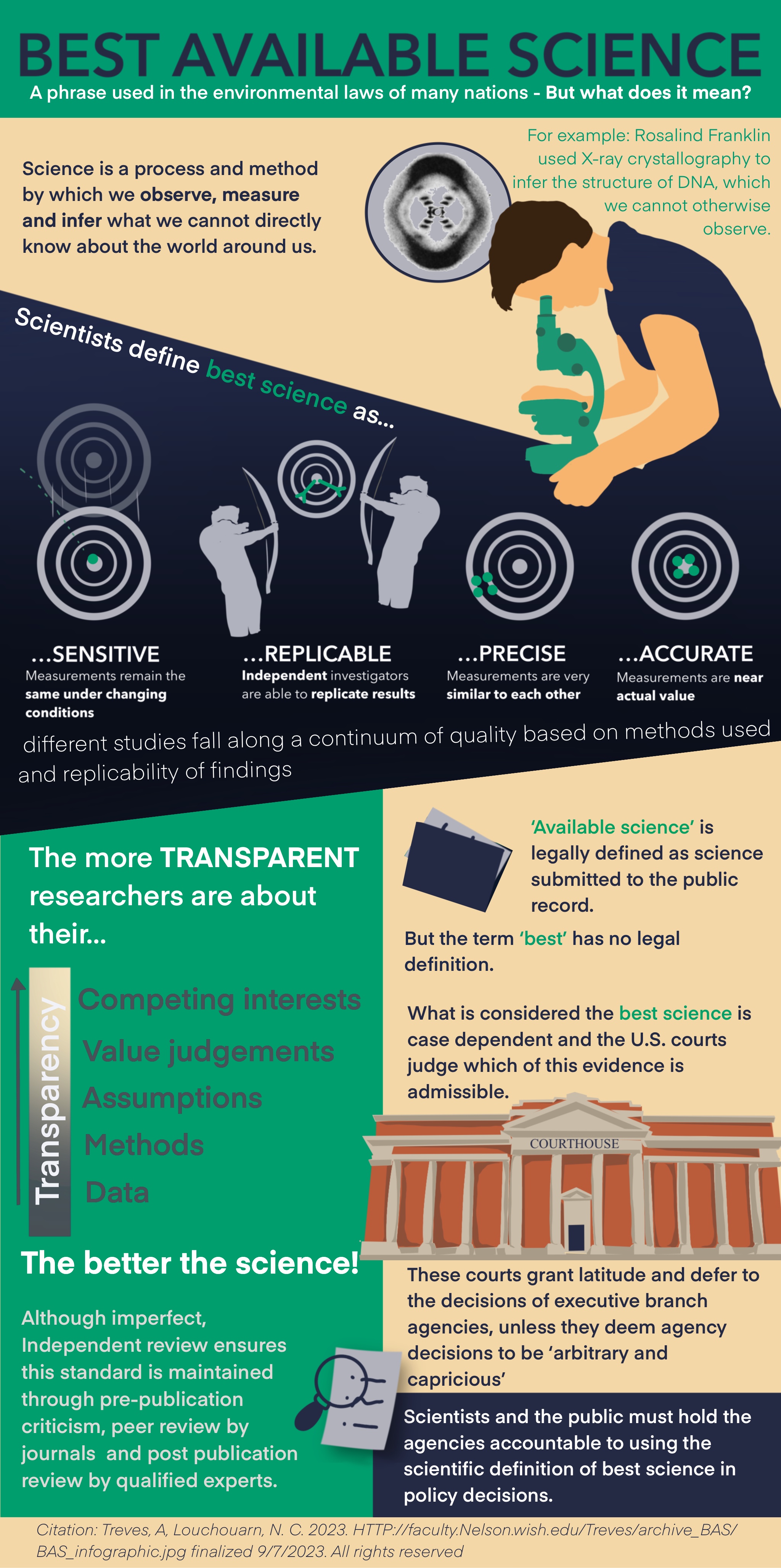
Treves A, Elbroch, LM, Koontz F, Papouchis CM. 2022.
How should scientific review and critique support policy? PLoS One Comment on Laundre & Papouchis 2020. Click here to access PLoS One pages
and full disclosure for the Comment
Treves, A., Elbroch, L.M. 2022.
Does killing wild carnivores raise risk for domestic animals? Wild Felid Monitor, the newsletter of the Wild Felid Research & Management Association. Summer 2022.
Low-stress livestock handling protects cattle in a five-predator habitat. PeerJ 11:e14788 http://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14788.
Supplementary Materials for the above article here.
Santiago-Ávila FJ, Agan S, W.,, Hinton JW, Treves A. 2022.
Evaluating how management policies affect red wolf mortality and disappearance. Royal Society Open Science 9:210400. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.210400.
Reply to Stauffer et al.: Uncertainty and precaution in hunting wolves twice in a year: in review at PLoS One available here.
In summary, our rebuttals to Roberts et al. and Stauffer et al, showed how
a. Stauffer et al.’s 2021 model of wolf occupancy in WI relies on data from previous years of winter tracking even if lethal management (such as a wolf-hunt) happened. Therefore, they are likely to be counting dead wolves as alive. That is why no one should trust the state estimate of the wolf population. If Stauffer and Roberts shared data as required by publication ethics, they might be able to support their estimates and their claims. But they have refused to share data again and again since 2012. And even if they did share their Datta we doubt it would show what they claim, so we suspect the state wolf population was lower than what they estimated in all previous years.
b. State estimates of birth rates are based on flawed science that hasn't passed peer review. The methods they use are inaccurate, even A. Wydeven admitted it in 2004, and they presume theirs are superior to mark-recapture methods published by Dick Thiel.
c. State estimates of wolf mortality are large, systematic under-estimates. Roberts and Stauffer both perpetuate a myth that radio-collared wolves who disappear just went off the air because of transmitter or battery failures despite the rate of disappearance being two- to three-fold higher than rates of disappearance for other (non-wolf) animal telemetry data.
d. Neither Stauffer nor Roberts share data so their claims are not credible by current scientific standards of the Open science movement. Neither they nor their co-authors transparently disclose potentially competing interests -- both financial and non-financial. These are breaches of publication ethics and research integrity according to the National Academies of science. We’re working with editors of multiple journals to flag their articles for concern or correction. The evidence for our claims is here. I will remove the disclosures they should have made once resolved. For now they are posted here .
The above evidence of undisclosed affiliations, and interests, both financial and non-financial. These are breaches of scientific integrity long described by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
Note Stauffer et al. and Roberts et al., claim we are trying to silence them when we are obviously trying the opposite, to compel transparency about their potentially competing interests, see this article on competing interests.
See this editorial Treves, A. 2024. Authors declare no competing interests—really? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (guest editorial) to understand why disclosures of potentially competing interests are important and why current practices in scientific peer review need an overhaul.
They also routinely engage in selective citation which means they do not cite the work that contradicts their preferred findings and whenever they are compelled to cite contrary findings, they mention rebuttals to it. This creates the illusion that their science is ironclad while critics have been challenged. Such cherry-picking or selective citation also violates National Academies guidelines on research integrity. Ti also further undermines claims that Wisconsin DNR policy is informed by the best available science, let alone 'science-based'.
I explain why scientific integrity is so important to public confidence in our research community and good government at this page.
Treves, A., Louchouarn, N.X. 2022.
Uncertainty and precaution in hunting wolves twice in a year. PLoS One, 2022. 17(3): e0259604. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0259604.
Note the debate about the above article continued into 2025 including corrections, rebuttals, and requests for retraction of work by Stenglein, van Deelen, and Stauffer. See above for details.
The DNR and NRB documents we cited from 2021.
Oliveira, Treves, López-Bao, Krofel, 2021. The contribution of the LIFE program to mitigating damages caused by large carnivores in Europe. Global Ecology and Conservation 31:e01815.
The Supplementary Information from Treves & Louchouarn 2022.
Santiago-Ávila, F.J. & Treves, A. 2022.Poaching of protected wolves fluctuated seasonally and with non-wolf hunting. Scientific Reports 12:e1738. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05679-w.
Treves, A., F.J. Santiago-Ávila, and K. Putrevu 2021.
Quantifying the effects of delisting wolves after the first state began lethal management. PeerJ, 9:e11666, doc 10.7717/peerj.11666.
Treves A, Paquet PC, Artelle KA, Cornman AM, Krofel M, Darimont CT. 2021.
Transparency about values and assertions of fact in natural resource management. Frontiers in Conservation Science: Human-Wildlife Dynamics, 2:e631998, doc 10.3389/fcosc.2021.631998.
Improved disclosures of non-financial competing interests would promote independent review. Academia Letters, 2021. Article 514: p. 1-9.
Agan, S.W., A. Treves, and E.L. Willey 2021.
Estimating poaching risk for the critically endangered wild red wolf (Canis rufus). PLoS One, 2021. 16(5):e0244261. DOI 10.1371.
Agan, S.W., A. Treves, and E.L. Willey 2021.
Majority positive attitudes cannot protect red wolves (Canis rufus) from a minority willing to kill illegally. Biological Conservation 109321. DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2021.109321
Louchouarn NX, Santiago-Ávila FJ, Parsons DR, Treves A.2021.
Evaluating how lethal management affects poaching of Mexican wolves. Royal Society Open Science 8 (registered report):: e2003300.
Just Preservation
In 2018, we published our ethic of public trusteeship, non-anthropocentric, multispecies justice that presents a method to give voice to future generations and to nonhumans when decisions are made to allocate or preserve nature. Start here with the original article Treves, A., Santiago-Ávila, F., Lynn, W.S. (equal co-authors) 2018. Just Preservation. Biological Conservation 229: 134-141.
The newest discussion of Just Preservation played out in 2021 in the journal Animal Sentience, which included commentaries by several dozen colleagues and our replies to each: F.J. Santiago-Ávila, A. Treves (equal co-authors), W.S. Lynn, Just preservation, trusteeship and multispecies justice. Animal Sentience 393. This continues our work on trusteeship, legal standing for nonhumans, and future generations, and equitable consideration of nonhumans as members of our moral community.
Treves, A. and N. J. Balster (2021)
The effect of extended student hours on performance of students in an interdisciplinary, introductory undergraduate ecology course. North American Colleges and Teachers of Agriculture Journal, 65:26-32.
Leopards and mesopredators as indicators of mammalian species richness across diverse landscapes of South Africa. Ecological Indicators 121, 107201.
by Abi Fergus, M.S. December 2020.
Santiago-Ávila, F.J., R.J. Chappell, and A. Treves, 2020.
Liberalizing the killing of endangered wolves was associated with more disappearances of collared individuals in Wisconsin, USA. Scientific Reports 10:e13881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70837-x.
Darimont, C.T., Hall, H., Mihalik, I., Artelle, K.A., Eckert, L., Treves A., Paquet, P.
Large carnivore hunting and the social license to hunt. Conservation Biology 35(4):1111-1119. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13657.
Carroll, C., Rohlf, D.J., von Holdt, B.M., Treves, A., Hendricks, S.A. 2020
Wolf delisting challenges demonstrate need for an improved framework for conserving intraspecific variation under the Endangered Species Act. Bioscience 125,1-12. doi:10.1093/biosci/biaa125. .
With a podcast from four of the authors to explain the analysis and recommendations, in the wake of 2020 Trump Administration rule to delist the gray wolf nationwide Listen here (55 minutes).
Treves, Louchouarn, Santiago-Ávila. 2020.
Modelling concerns confound evaluations of legal wolf-killing. Biological Conservation. 249:108643, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108643.
Treves & Santiago-Ávila. 2020
Myths and assumptions about human-wildlife conflict and coexistence. Conservation Biology 10.1111/cobi.13472.
Standards of evidence in wild animal research. A report for the Brooks Institute for Animal Rights Law and Policy.
Treves 2020. Elephants and pandemics. Animal Sentience 28(20). URL
Treves, A., Krofel M, Ohrens O and van Eeden 2019
Predator Control Needs a Standard of Unbiased Randomized Experiments With Cross-Over Design. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 7:402-413. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2019.00462
Scientific ethics and the illusion of naïve objectivity. (guest editorial) Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:1.
Trophy hunting: Insufficient evidence. Letter in Science 366(6464):435.
Ohrens, O., Bonacic, C., Treves, A. 2019. Non-lethal defense of livestock against predators: Flashing lights deter puma attacks in Chile. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 17(1):1-7.
van Eeden, L., Eklund, A., Miller, J.R.B.,...17 co-authors... Treves, A. (equal first authors) 2018. Carnivore conservation needs evidence-based livestock protection. PLOS Biology https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2005577
2018. Van Eeden, Treves, Ritchie. The Conversation.
A short popular science summary of the above article.
Treves, A., Artelle, K.A., Paquet, P.C. 2018. Differentiating between regulations and hunting as conservation interventions. Conservation Biology 33(2):472–475. DOI:10.1111/cobi.13211.
Santiago-Avila, F.J., Lynn, W.S., Treves, A. 2018.
Inappropriate consideration of animal interests in predator management: Towards a comprehensive moral code. In Large Carnivore Conservation and Management: Human Dimensions and Governance, ed. T. Hovardos, Taylor & Francis, London.
Ohrens, O., Santiago-Avila, F.J., Treves, A.2019.
The challenges of preventing real and perceived threats to livestock. In Human-Wildlife Interactions: Turning Conflict into Coexistence, eds. B. Frank, S. Marchini, J. Glikman, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
Intergenerational equity can help to prevent climate change and extinction. Nature Ecology & Evolution DOI: 10.1038/s41559-018-0465-y.
Supporting Data.
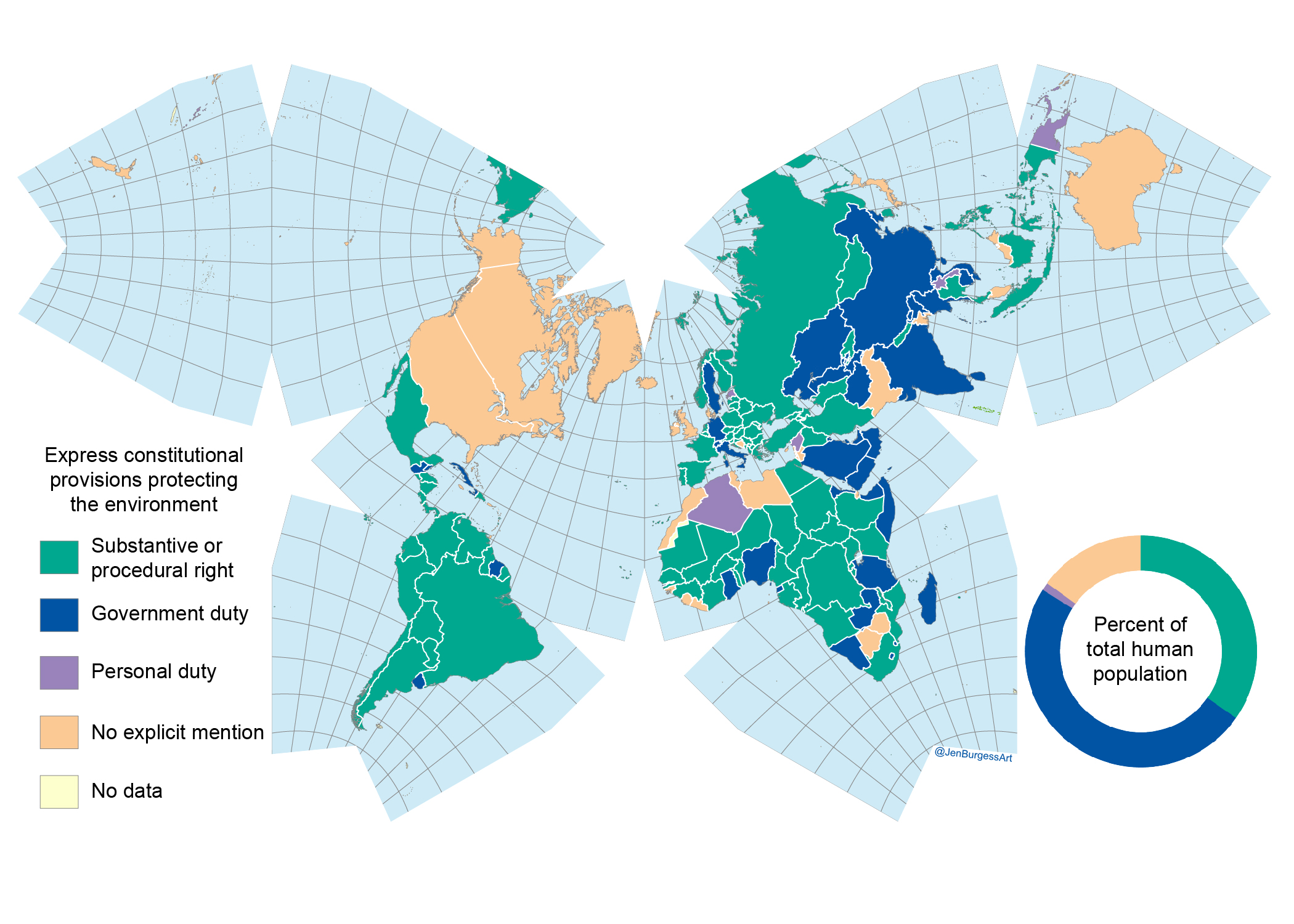 Credit: Jen Burgess @jenburgessart
Credit: Jen Burgess @jenburgessart
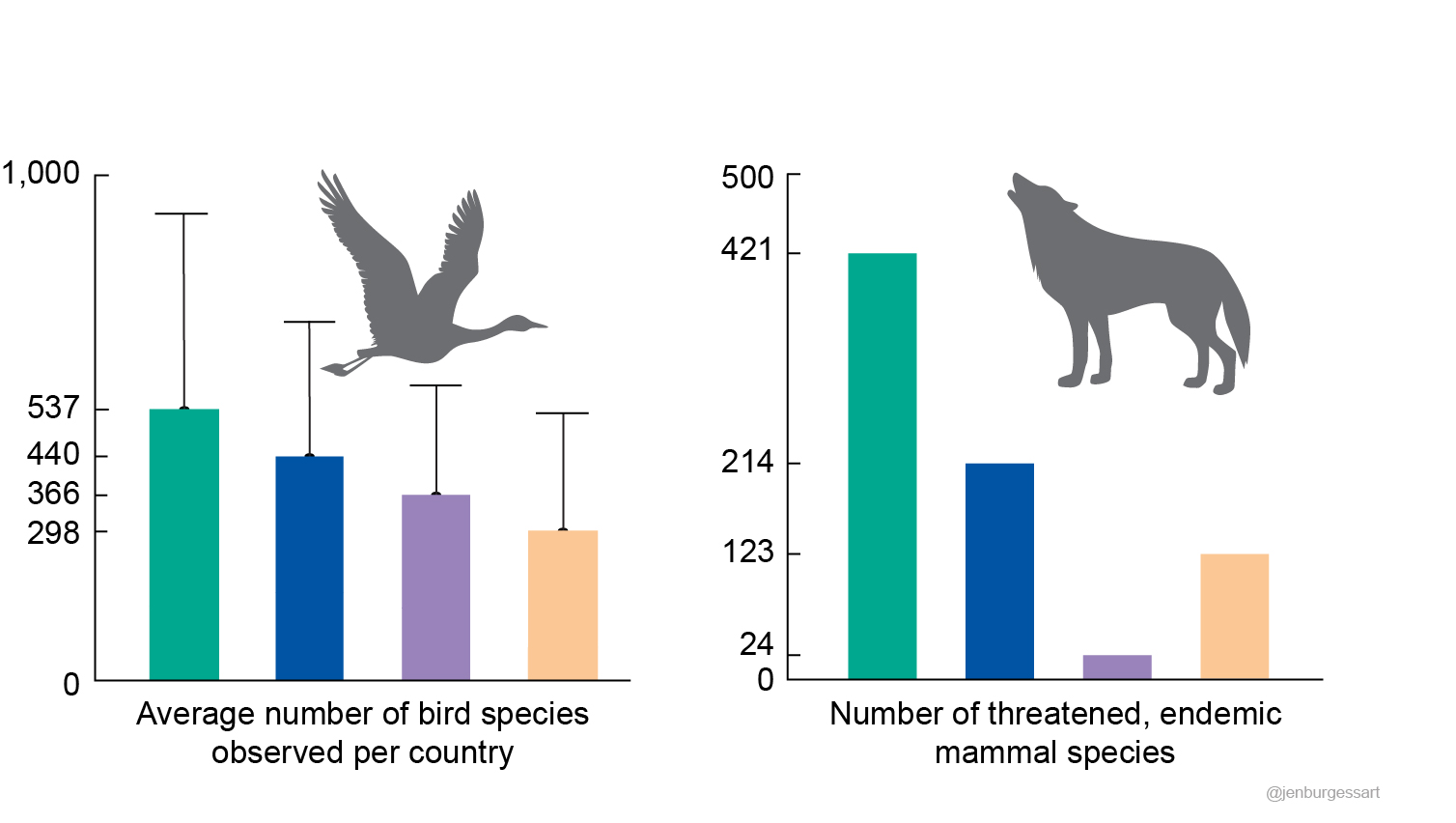
Credit: Jen Burgess @jenburgessart
Infographic below for 'Hallmarks of science missing from North American wildlife hunting and trapping plans':

Artelle, K.A., Reynolds, J.D., Treves, A. Walsh, J.C., Paquet, P.C., Darimont, C.T. 2018.
Hallmarks of science missing from North American wildlife management. Science Advances. 2018.
short video explaining the findings
Santiago-Avila, F.J., Cornman, A.M., Treves, A. 2018.
Killing wolves to prevent predation on livestock may protect one farm but harm neighbors. PLOS One 13:e0189729 here
Treves A, Rabenhorst MF. 2017.
Risk Map for Wolf Threats to Livestock still Predictive 5 Years after Construction. PLoS ONE: http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0180043.
Lopez-Bao, J.V., Chapron, G., Treves, A. 2017.
The Achilles heel of participatory conservation. Biological Conservation 212: 139-143.
Treves, A., Artelle, K.A., Darimont, C.T., Parsons, D.R. 2017.
Mismeasured mortality: correcting estimates of wolf poaching in the United States. Journal of Mammalogy 98(3): open access at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jmammal/gyx052.
Darimont, C.T., Paquet, P., Treves, A., Artelle, K.A., Chapron, G. 2018. Political populations of large carnivores.Conservation Biology 32(3):747-749.
Carroll, C., B. Hartl, G.T. Goldman, D.J. Rohlf, A. Treves, J.T. Kerr, E.G. Ritchie, R.T. Kingsford, K.E. Gibbs, M. Maron, J.E.M Watson. 2017. Defending scientific integrity in conservation policy processes: lessons from Canada, Australia, and the United States. Conservation Biology DOI: 10.1111/cobi.12958
Treves, A., J.A. Langenberg, J.v. López-Bao, M.F. Rabenhorst 2017. Gray wolf mortality patterns in Wisconsin from 1979 to 2012 Journal of Mammalogy 98(1): DOI:10.1093/jmammal/gyw145
Chapron, G. and A. Treves 2016a and b, 2017a and b.
In 2016, Chapron & Treves published the first challenge to the notion that legal killing reduces illegal killing of wolves, a notion which had been put forward by The US government in a court case about protections for gray wolves. Chapron & Treves (2016a,b) presented population dynamic evidence that the opposite occurred, liberalizing wolf-killing increased wolf-poaching. This was challenged without new evidence by Pepin et al., Stien, and Olson et al. in 2017, so the debate simmered until 2020 when Dr. Francisco Santiago-Ávila et al. presented estimates of gray wolf survival and incidence of death and disappearance among radio-collared Wisconsin wolves. The data presented no evidence that liberalizing wolf-killing did anything good for the wolves as individuals or as a population. Those researchers formulated the hypothesis of facilitated illegal killing. That hypothesis was replicated for Mexican gray wolves in Arizona and New Mexico by Louchouarn et al. 2021 and for North Carolina red wolves by Santiago-Ávila et al. 2022. Also in 2022 and 2023, two new analyses of Wisconsin and Michigan gray wolves reaffirmed the inter-annual increases in deaths and disappearances during periods characterized by different policies, different mammal-hunting seasons, and different political administrations (Santiago-Ávila & Treves 2022; Louchouarn 2023). Breck et al. (2023) published a contrary view of Mexican gray wolf removals but their analysis has also been questioned on multiple methodological grounds. Although the scientific debate is unresolved, the discussion has advanced measurably in the rigor of scientific analysis and the quality of evidence. In my opinion the balance of evidence is that policies and politics that reduce the value of wolves or encourage lawlessness contribute to wolf-poaching. And liberalizing and expanding wolf-killing has been the major cause of devaluing wolves in many regions.
Since 2018, the debate in Nordic countries has been equivocal with Liberg et al. (2020) arguing that regulated wolf-hunting lowered poaching, a conclusion challenged by Treves et al. (2020) on the basis of the same data. Also in Finland, Surtainen & Kojola (2017, 2018) reported that legal killing removed gray wolves before poachers could do so and that regulated killing was not a solution to illegal killing in Finland. Although the scientific debate is unresolved, the discussion has advanced measurably in the rigor of scientific analysis and the quality of evidence. In my opinion the balance of evidence is that policies and politics that reduce the value of wolves or encourage lawlessness contribute to wolf-poaching. And liberalizing and expanding wolf-killing has been the major cause of devaluing wolves in many regions.
See the Publications page for references to Treves, Chapron, Santiago-Ávila, and Louchouarn. For other references, please contact
Treves, A., Krofel, M., McManus, J. (equal co-authors).2016.
Predator control should not be a shot in the dark. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment14: 380-388. This article has the highest Altmetric score among articles of the same age in that journal, ranks in the 99th percentile for all research outputs of similar age, and the top 5% for research outputs of all types and ages; see https://wiley.altmetric.com/details/10981879#score for details.
In a nutshell:
• Predator control methods to prevent livestock loss have rarely been subject to rigorous tests using the "gold standard"
for scientific inference (random assignment to control and treatment groups with experimental designs that avoid biases in sampling, treatment, measurement, or reporting).
• Across the controlled experiments that we systematically examined, higher standards of evidence were generally applied in tests of non-lethal methods than in tests of lethal methods for predator control.
• Non-lethal methods were more effective than lethal methods in preventing carnivore predation on livestock generally; at least two lethal methods (government culling or regulated, public hunting) were followed by increases in predation on livestock; zero tests of non-lethal methods had counterproductive effects.
• All flawed tests came from North America; ten of 12 flawed tests were published in three journals, compared to four of 12 tests with strong inference in those same journals.
• We recommend suspending lethal predator control methods that do not currently have rigorous evidence for functional effectiveness in preventing livestock loss until gold- standard tests are completed.
Treves, A., Bonacic, C.(equal co-authors). 2016.
Humanity's Dual Response to Dogs and Wolves. Trends in Ecology and Evolution (TREE). doi:10.1016/j.tree.2016.04.006
Take-home message: The relationship between humans, dogs, and wolves has changed over more than 40,000 years in ways that reflect the ecology and evolved traits of all three species.
Ripple, W. With 41 co-authors authors including Treves. 2017.
Conserving the World’s Megafauna and Biodiversity: The Fierce Urgency of Now. Bioscience. doi:10.1093/biosci/biw168
Ripple, W. With 43 co-authors including A. Treves 2017.
Saving the World’s Terrestrial Megafauna. BioScience. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biw092
Treves, A., C. Browne-Nunez, J. Hogberg, J. Karlsson Frank, L. Naughton-Treves, N. Rust, Z. Voyles 2017. Estimating poaching opportunity and potential, in Conservation Criminology, M.L. Gore, Editor. John Wiley & Sons: New York. p. 197-212.
A conceptual framework for understanding illegal killing of large carnivores. Ambio 46(3): 251–264.
Treves, A., Chapron, G., Lopez-Bao, J.V., Shoemaker, S., Goeckner, A., Bruskotter, J.T. 2015.
Predators and the Public Trust. Biological Reviews doi: 10.1111/brv.12227.
Take-home messages: Democratic governments have a duty under the public trust to preserve wildlife for current and future generations without substantial impairment. Trust duties are fiduciary duties meaning transparent accounting and prudence at a minimum. Few trustees of predators have lived up to these legal and ethical standards.
Krofel, M., Treves, A., López-Bao, J.V. 2015.
Hunted carnivores at outsized risk. Science. 350: 6260.
Take-home message: Large carnivores are particularly vulnerable to human-induced mortality and we still now little about how they respond.
Treves, A. Bruskotter, J.T. 2014.
Tolerance for Predatory Wildlife. Science 344: 476-477.
Take-home messages: Tolerance for predators did not reflect individual economic losses but rather social identity and peer group complaints. Intolerance for wolves and inclinations to poach wolves rose when the government culled wolves. Tolerance for wolves did not increase when wolf hunting and trapping season was implemented.
Ohrens, O., Treves, A., Bonacic, C. 2015.
Relationship between rural depopulation and puma-human conflict in the high Andes of Chile. Environmental Conservation doi:10.1017/S0376892915000259.
Voyles, Z., Treves, A., Macfarland, D. 2015.
Spatiotemporal effects of nuisance black bear management actions in Wisconsin. Ursus 26: 11-20.
Hogberg, J., Treves, A., Shaw, B., Naughton-Treves, L. 2015.
Changes in attitudes toward wolves before and after an inaugural public hunting and trapping season: early evidence from Wisconsin’s wolf range. Environmental Conservation, doi 10.1017/S037689291500017X.
Browne-Nuñez, C., Treves, A., Macfarland, D., Voyles, Z., Turng, C. 2015.
Tolerance of wolves in Wisconsin: A mixed-methods examination of policy effects on attitudes and behavioral inclinations. Biological Conservation 189: 59-71.
Olson, E.R., Treves, A., Wydeven, A.P., Ventura, S. 2014.
Landscape predictors of wolf attacks on bear-hunting dogs in Wisconsin, USA. Wildlife Research 41: 584–597.
Bruskotter, J.T., Vucetich, J.A., Enzler, S., Treves, A., Nelson, M.P. 2013.
Removing protections for wolves and the future of the U.S. Endangered Species Act (1973). Conservation Letters 7: 401-407.
Carnivore Management. pp. 83-90 in B.S. Steel editor. Science and Politics: An A-To-Z Guide to Issues and Controversies. CQ Press, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA. Treves, A., Naughton-Treves, L., Shelley, V. 2013.Longitudinal Analysis of Attitudes Toward Wolves. Conservation Biology 27: 315–323
Tolerant attitudes reflect an intent to steward: A Reply to Bruskotter and Fulton. Society and Natural Resources 25: 103-104.
Shelley, V., Treves, A., Naughton, L. 2011. Attitudes to Wolves and Wolf Policy Among Ojibwe Tribal Members and Non-tribal Residents of Wisconsin's Wolf Range. Human Dimensions of Wildlife 16: 397-413.
Treves, A., Bruskotter, J. 2011. Gray Wolf Conservation at a Crossroads. BioScience 61: 584-585.
2012. Bruskotter, J., Enzler, S., Treves, A. Rescuing Wolves from Politics: Wildlife as a Public Trust Resource. Response to Mech and Johns. Science (Wash., D.C.), Policy Forum 335: 795-796.
2011. Bruskotter, J., Enzler, S., Treves, A. Rescuing Wolves from Politics: Wildlife as a Public Trust Resource. Science (Wash., D.C.), Policy Forum 333(6051): 1828-1829.
Hunters as stewards of wolves in Wisconsin and the Northern Rocky Mountains, USA. Society and Natural Resources 24: 984-994.
Treves, A., Martin K.A., Wydeven, A.P., Wiedenhoeft, J.E. 2011. Forecasting Environmental Hazards and the Application of Risk Maps to Predator Attacks on Livestock. Bioscience 61(6): 451-458.
Schloegel, C., Jones, T., Zug, B., Achig, L., Treves, A. 2011. Don Oso Program Develops Participatory Monitoring Protocol for Andean Bears in Southern Sangay National Park, Ecuador. International Bear News 20(2): 23-25.
Strategic trade-offs for wildlife-friendly eco-labels. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 8(9): 491–498.
Treves, A., Kapp, K.J., Macfarland, D.M. 2010. American black bear nuisance complaints and hunter take. Ursus 21(1):30-42.
Treves, A., Mwima, P., Plumptre, A.J., Isoke, S. 2010. Camera-trapping forest-woodland wildlife of western Uganda reveals how gregariousness biases estimates of relative abundance and distribution. Biological Conservation. 143: 521-528.
Hunting for large carnivore conservation. Journal of Applied Ecology 46: 1350-1356.
Treves, A., Jurewicz, R., Naughton-Treves, L., Wilcove, D. 2009. The price of tolerance: wolf damage payments after recovery. Biodiversity and Conservation, 2009, 18(14):4003-4021.
Treves, A., Wallace, R.B., White, S. 2009. Participatory planning of interventions to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts. Conservation Biology 2009, 23(6): 1577-1587.
Treves, A., Plumptre, A.J., Hunter, L.T.B., Ziwa, J. 2009. Identifying a potential lion Panthera leo stronghold in Queen Elizabeth National Park, Uganda, and Parc National des Virunga, Democratic Republic of Congo. Oryx 43(1): 60-66. (Copyright Cambridge University Press http://journals.cambridge.org/repo_A35fUJfB) and see the we published as a correction to this manuscript.
Beyond Recovery: Wisconsin's Wolf Policy 1980-2008. Human Dimensions of Wildlife 13(5): 329-338. Human-wildlife conflicts around protected areas. In Wildlife and Society: The Science of Human Dimensions. Manfredo, M., Vaske, J. J., Brown, P., Decker, D.J., Duke, E.A. eds. Island press, Washington, DC.
Treves, A., Martin, K.A., Wiedenhoeft, J.E., Wydeven, A.P. 2009. Gray wolf dispersal in the Great Lakes Region, in Recovery of Gray Wolves in the Great Lakes Region of the United States: an Endangered Species Success Story. Wydeven, A. P., Heske, E.H., Van Deelen, T. R. eds. Springer: New York.
Treves, A., Palmqvist, P. 2007. Reconstructing hominin interactions with mammalian carnivores (6.0 - 1.8 Ma) in Primate Anti-Predator Strategies. K. A. I. Nekaris, and S. L. Gursky, eds. Springer, New York.
Sillero-Zubiri, C., Sukumar, R., Treves, A. 2007. Living with wildlife: the roots of conflict and the solutions. In: Key Topics in Conservation Biology. D. MacDonald and K. Service, eds. Oxford, Oxford University Press, pp. 266-272.
Treves, A., Wallace, R.B., Naughton-Treves, L., Morales, A. 2006. Co-managing human-wildlife conflicts: A review. Human Dimensions of Wildlife 11(6):1-14.
Or you can read the
Treves, A., Andriamampianina, L., Didier, K., Gibson, J,. Plumptre, A., Wilkie, D., Zahler, P. 2006. A simple, cost-effective method for involving stakeholders in spatial assessments of threats to biodiversity. Human Dimensions of Wildlife 11(1): 43-54.
Treves, A., Naughton-Treves, L. 2005. Evaluating lethal control in the management of human-wildlife conflict. People and Wildlife, Conflict or Coexistence? Woodroffe, R., Thirgood, S., Rabinowitz, A. eds. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. pp. 86-106.
Tourism impacts on the behavior of black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra) at Lamanai, Belize. In Commensalism and Conflict: The primate-human interface. J. Paterson & J. Wallis, eds. American Society of Primatology, Norman, OK.
Naughton-Treves, L., Treves, A. 2005. Socioecological factors shaping local tolerance of crop loss to wildlife in Africa. People and Wildlife, Conflict or Coexistence? Woodroffe, R., Thirgood, S., Rabinowitz, A. eds. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK. pp. 253-277.
Treves, A., Naughton-Treves, L. Harper, E., Mladenoff, D., Rose, R., Sickley, T., Wydeven, A. 2004. Predicting human-carnivore conflict: A spatial model derived from 25 years of wolf predation on livestock. Conservation Biology 18(1): 114-125.
Wydeven, A.P., Treves, A., Brost, B., Wiedenhoeft, J. 2004. Characteristics of wolf packs in Wisconsin: Identification of traits influencing depredation. Pp. 28-50 in People and Predators: From Conflict to Coexistence. N. Fascione, A. Delach, M. Smith, eds. Island Press, Washington, DC. Treves, A., Karanth, K.U. 2003. Human-carnivore conflict and perspectives on carnivore management worldwide. Conservation Biology 17(6): 1491-1499.
Grossberg, R., Treves, A., Naughton-Treves, L. 2003. Incidental ecotourism at Lamanai, Belize: The incidental ecotourist - Measuring visitor impacts on endangered howler monkeys inhabiting an archaeological site in Belize. Environmental Conservation 30(1): 40-51.
Naughton-Treves, L., Grossberg, R., Treves, A. 2003. Paying for tolerance: The impact of livestock depredation and compensation payments on rural citizens' attitudes toward wolves. Conservation Biology 17(6): 1500-1511.
Naughton-Treves, L., Mena, J.L., Treves, A., Alvarez, N., Radeloff, V.C. 2003. Wildlife survival beyond park boundaries: The impact of swidden agriculture and hunting on mammals in Tambopata, Peru. Conservation Biology 17(4): 1106-1117.
Shivik, J.A., Treves, A., Callahan, M. 2003. Nonlethal techniques for managing predation: primary and secondary repellents. Conservation Biology 17(6): 1531-1537.
Treves, A., Jurewicz, R., Naughton-Treves, L., Rose, R., Willging, R., Wydeven, A. 2002. Wolf depredation on domestic animals in Wisconsin, 1976-2000. Wildlife Society Bulletin 30:231-241.
Culminating Treves' research on primate vigilance, the following article also has relevance to predator-prey behavioral ecology more generally. Treves, A. 2000. Theory and method in studies of vigilance and aggregation. Animal Behaviour (Review Article) 60:711-722. Treves, A., Naughton-Treves, L. 1999. Risk and opportunity for humans coexisting with large carnivores. Journal of Human Evolution 36: 275-282.
Naughton-Treves, L., Treves, A., Chapman, C., Wrangham, R.W. 1998. Temporal patterns of crop raiding by primates: Linking food availability in croplands and adjacent forest. Journal of Applied Ecology 35(4): 596-606. For earlier articles about primate behavioral ecology, Adrian Treves.